Coupling an underflow model to a 3D hydrodynamic model
ABSTRACT: A separate underflow model is coupled to the three-dimensional (3D) estuary and lake computer model. The underflow equations are solved on a two-dimensional (2D) grid underlying the 3D model grid. The underflow model entrains ambient water whose properties are given by the fluid properties of the bottom boundary cells in the 3D model. This new approach allows improved representation of underflow effects in z-coordinate models by reducing numerical convective entrainment. An idealized case is used to illustrate the benefits of the underflow model. Comparisons of model results and field data for a saline underflow event in Lake Ogawara and a cold-water underflow in Lake Kinneret demonstrate improved model capability in representing underflow events that are thin compared to the vertical grid scale.
EXTRACT: Figure 2:
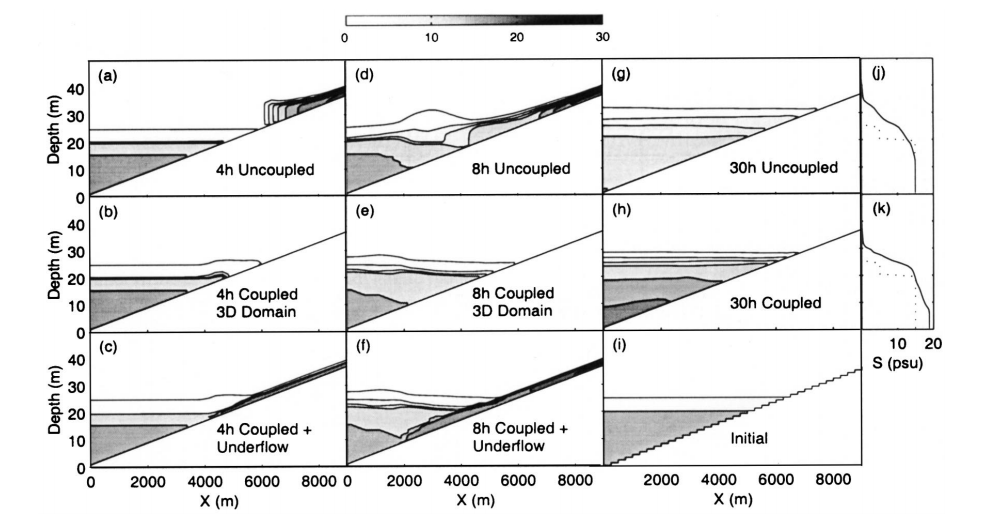
Fig. 2. Contours of salinity of idealized underflow event simulated by 3D ELCOM with and without underflow submodel 4 h (a–c), 8 h (d–f), and 30 h (g,h) after start of inflow. Salinity profiles at wall after 30 h are shown as solid lines in (j) and (k). Dotted lines show initial salinity profile, which is contoured in (i).
